What’s new in Percona Everest 1.4.0¶
Warning
Google Container Registry (GCR) is scheduled to be deprecated and will officially shut down on March 18, 2025. All versions of Percona Everest prior to 1.4.0 depend on images hosted on GCR, meaning that downloading those images will fail after the shutdown date. We strongly recommend upgrading to Percona Everest version 1.4.0 as soon as possible. If you do not upgrade, Percona Everest will no longer function.
For more details, refer to the Container Registry Deprecation documentation.
To begin your journey with Percona Everest, check out the Quickstart Guide for Percona Everest.
Release summary at a glance
| Sr. No | Release summary | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Helm charts | Simplify your Percona Everest deployments with Helm |
| 2. | Namespace management | Manage your namespaces with new everestctl commands |
| 3. | Improved edit database flow | Manage your namespaces with new everestctl commands |
| 4. | Operators support | Support for Percona Operator for MongoDB v1.18.0) (PSMDB) and Percona Operator for PostgreSQL v2.5.0 (PG) |
| 5. | New features | Check out the new features introduced in Percona Everest 1.4.0 |
| 6. | Improvements | Discover all the enhancements featured in Percona Everest 1.4.0 |
| 7. | Bugs | Find out about all the bugs fixed in Percona Everest 1.4.0 |
| 8. | Known limitations | Discover all the known limitations in Percona Everest 1.4.0 |
Release highlights¶
Simplify your Percona Everest deployments with Helm¶
We are excited to announce the launch of Helm charts in Percona Everest 1.4.0. Helm charts simplify the deployment process by packaging all necessary resources and configurations, making them ideal for automating and managing installations in Kubernetes environments.
Percona Helm charts can be found in percona/percona-helm-charts repository in Github.
If you are looking to get started with Percona Everest using Helm, check out our comprehensive documentation.
Additionally, check our Upgrade and Uninstall sections to find out how to upgrade or uninstall your Percona Everest instances using Helm.
Manage your namespaces with new everestctl commands¶
Namespace management is essential in Percona Everest for efficiently organizing, securing, and allocating resources, particularly in large and complex Kubernetes environments. By leveraging Kubernetes namespaces, Percona Everest achieves logical isolation, enhanced security, and better resource allocation for databases, backups, and monitoring setups.
Starting with Percona Everest 1.4.0, we have introduced new everestctl commands to manage your namespaces. These commands enable you to:
For a deep dive into managing namespaces for provisioning DB namespaces in Percona Everest, refer to our documentation.
Removal of the Edit DB Wizard for an enhanced User Experience¶
Starting with Percona Everest 1.4.0, we have removed the Edit DB wizard to provide a more streamlined user experience. You can now edit specific fields directly from the DB Overview page using our new editable widgets, eliminating the need to navigate through the entire Edit DB wizard.
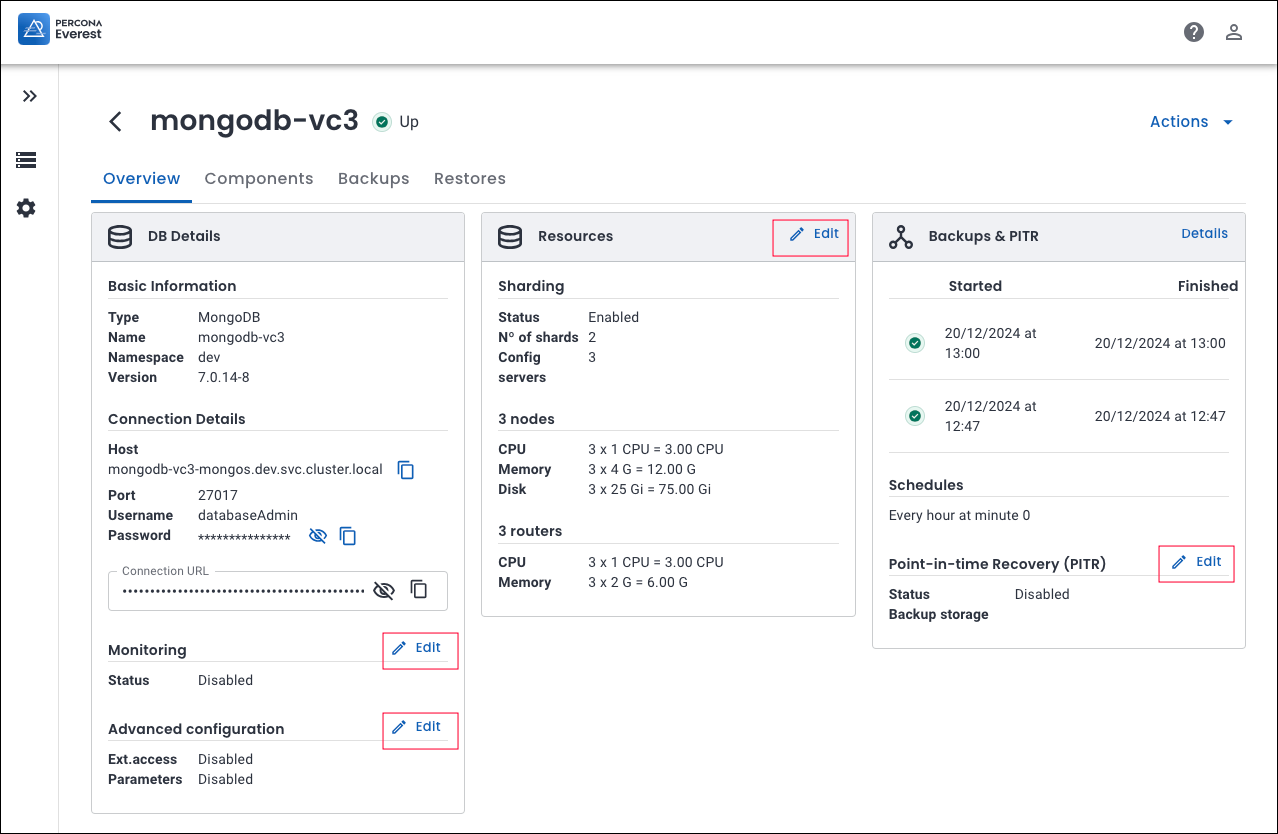
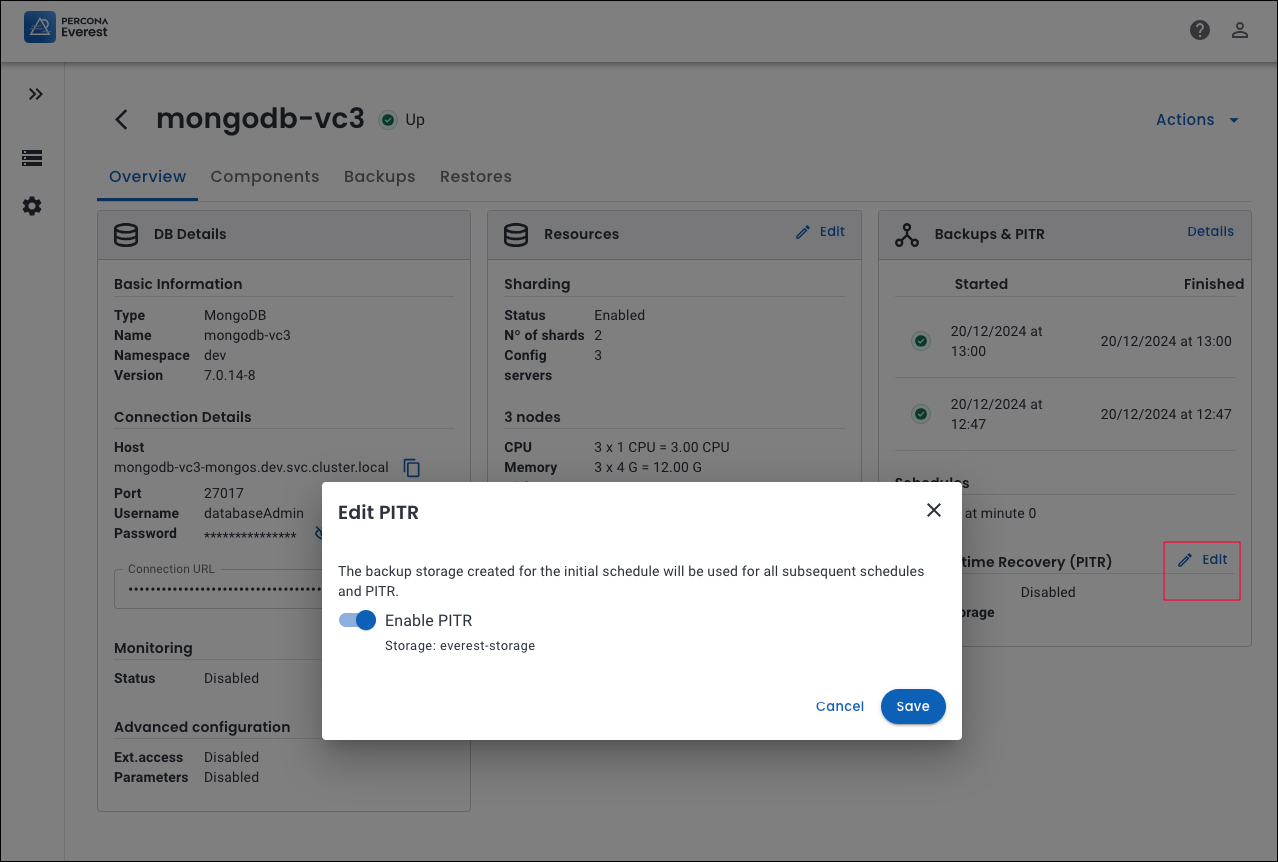
Let’s assume you want to make changes to Point-in-time-Recovery (PITR). First, navigate to the specific database. Then, go to Overview > Point-in-time-Recovery (PITR) and click Edit. Make the necessary changes and click Save.
Support for PSMDB 1.18.0 and PG 2.5.0¶
Starting with Percona Everest 1.4.0, we are thrilled to announce that we have added support for PSMDB Operator v1.18.0 and PG operator v2.5.0.
New features¶
-
EVEREST-1511: We have introduced Helm charts, which simplify the Percona Everest deployment process by packaging all necessary resources and configurations. These charts are ideal for automating and managing installations in Kubernetes environments.
-
EVEREST-1512: You can now seamlessly upgrade your Percona Everest installation using Helm, a package manager for Kubernetes. This streamlined process simplifies the upgrade experience.
-
EVEREST-1673: Starting with Percona Everest 1.4.0, we have introduced new
everestctlcommands to manage your namespaces. -
EVEREST-908: Starting with Percona Everest 1.4.0, the Overview page now includes the Connection URL in the Connection Details widget, allowing you to copy it directly.
-
EVEREST-1599: We have added support for PostgreSQL operator v2.5.0.
-
EVEREST-1624: We have added support for PSMDB Operator v1.18.0.
Improvements¶
-
EVEREST-1065: Starting with Percona Everest 1.4.0, we have removed the Edit button from the database list actions. This change provides a more streamlined user experience, allowing you to edit the database directly from the database Overview page without having to go through the entire edit wizard.
-
EVEREST-1066: We have improved the Backups & PITR widget on the database Overview page. With this enhancement, you can now directly enable or disable PITR by clicking Edit from this page.
-
EVEREST-1210: The Advanced Configuration panel on the DB Details widget is now more user-friendly than ever. You can edit or enable parameters directly from the database Overview page. Just click Edit, and and make your changes with ease.
-
EVEREST-1304: We have simplified the create database wizard. When you click Create Database, a menu with the MySQL, PostgreSQL, and MongoDB options will appear under the button. After selecting a database type, you will be guided to the wizard with the chosen value pre-set.
-
EVEREST-1546: You can see the number of proxies, routers, and bouncers, along with their resources, directly on the Database Summary and Overview pages. This enhancement provides greater visibility into the resources within your clusters.
-
EVEREST-1683: The Backups on the Overview page are organized in descending order, making it easier to find your most recent backups by their start date and time.
-
EVEREST-1686: We’ve adopted a 24-hour time format for our backups and restores to eliminate any potential confusion and ensure consistency across Percona Everest.
-
EVEREST-1687: The label for the upgrade CRD button has been shortened to improve readability.
-
EVEREST-1701: Starting with Percona Everest 1.4.0, when configuring RBAC policies, the resource name for
database-cluster-backupsnow corresponds to the database name instead of the backup name. This change allows for a more intuitive configuration of permissions for backups at the database level. -
EVEREST-1702: Starting with Percona Everest 1.4.0, when configuring RBAC policies, the resource name for
database-cluster-restoresnow corresponds to the database name instead of the restore name. This change allows for a more intuitive configuration of permissions for backups at the database level.
Bugs¶
-
EVEREST-1688: If a user changed the value for the number of shards and then scrolled down, the number of shards would unexpectedly increase. Conversely, if they scrolled up, the number of shards would decrease. The value did not remain constant, and similar behavior was observed in other fields as well. This issue has been resolved now, and the values for the fields remain constant.
-
EVEREST-1187: We’ve resolved the issue that prevented Point-In-Time Recovery (PITR) from being enabled for the PostgreSQL database after setting up backup schedules on the Backups page.
-
EVEREST-1235, EVEREST-1254:
everestctlnow provides relevant error messages when using theinstallcommand, helping you identify any issues that occurred during the installation process. For instance, if the kubeconfig is unavailable, the cluster configuration is incorrect, or the cluster cannot be connected to,everestctlwill display an appropriate error message. -
EVEREST-1254: During the uninstallation of Percona Everest, an unusual error code appeared at the end of the process. The issue has been resolved now.
-
EVEREST-1320: The warning message for a gap in Point-in-Time Recovery (PITR) is now shown on both the Backups and Restores pages. Additionally, when the database is up and running, a triangle icon on the dashboard page now correctly directs you to the Backups page.
-
EVEREST-1352: To ensure data integrity, all database actions are now disabled while the database is in a Deleting state.
-
EVEREST-1399: The Resource per node now accurately displays the value set during database creation. Previously, there was a mismatch between the value chosen at setup and what was shown when editing the database. Instead, it defaulted to Custom, which was not the initial selection.
-
EVEREST-1407: We’ve resolved an issue where a user lacking the necessary RBAC permissions could access specific information in Percona Everest.
-
EVEREST-1440: We’ve resolved an issue that caused a delay while loading the Backups page. Furthermore, the Add Storage option was displayed on the Backups page even though the user did not have backup storage permissions.
-
EVEREST-1518, EVEREST-1604: We’ve resolved an issue that permitted users to view and edit DB clusters, as well as restore to the same DB cluster, even if they lacked the necessary permissions for the database engine(s).
-
EVEREST-1534 The Database clusters page was empty for users with access to only one database cluster. This issue has now been resolved.
-
EVEREST-1565: The MongoDB versions are now sorted in descending order, and all the versions are visible on the Basic information page when selecting the Database version.
-
EVEREST-1593: We’ve resolved an issue that was preventing the display name and database version from showing up during a new cluster creation.
-
EVEREST-1594: Scheduled backups failed after several successful runs when the number of shards in the MongoDB sharded cluster was modified. This issue has been resolved now.
-
EVEREST-1608: Percona Everest now displays an error message if the Proxies value in the Custom field for the MySQL database is not entered. Also, unless you enter this value, the Continue button is disabled, which aligns with the expected behavior.
-
EVEREST-1613: On the Edit Topology page, the Resource Size per Node field now displays the initially selected configuration. Previously, when reopening the Edit Topology page, the setting would revert to Custom instead of retaining the chosen option.
-
EVEREST-1615: We have fixed an issue where the uninstallation of Percona Everest failed if a MongoDB sharded cluster was in the Deleting state.
-
EVEREST-1642: When restoring to a new database, modifying its version is no longer possible. This behavior aligns with the expected functionality of Percona Everest.
-
EVEREST-1649: We’ve addressed an issue that caused the Add storage button for backups to remain inactive, even after the page was refreshed. The button would only become active when users switched between different tabs, such as transitioning from the Overview tab to the Backups tab.
-
EVEREST-1650: We have resolved an issue on the Backups page where the button incorrectly displayed Add storage instead of Create backup after adding new storage. This prevented users from creating backups. The issue occurred when trying to add backup storage in a namespace other than the one where the database was originally created (the default namespace).
-
EVEREST-1694: The Backup storages page was appearing empty for users with access to only one backup storage. This issue has now been resolved.
-
EVEREST-1695: The Monitoring endpoints page was empty for users with access to only one monitoring instance. This issue has now been resolved.
-
EVEREST-1703: While setting up a MongoDB sharded cluster in Percona Everest, an error occurred during the topology step. If only 1 config server was selected, an error message appeared, stating that the number of config servers must be greater than one. However, when the config server setting was changed to 3 or any other value, the “Next” button became grayed out, preventing progress to the next step. The issue has been resolved now.
-
EVEREST-1712: We’ve resolved an issue where the Percona Everest UI pages became unresponsive after some time. None of the page elements worked, and the only solution was to close the page and start a new browser session.
Known limitations¶
-
In Percona Operator for PostgreSQL version 2.5.0, backups start failing after a minor version upgrade from PostgreSQL 16.3 to 16.4 if monitoring is enabled on the database.
Workaround
Once you upgrade your PostgreSQL version, it’s essential to also update the
pg_stat_monitorextension by executing the following command:ALTER EXTENSION pg_stat_monitor UPDATE; -
The backup storage you choose for your initial backup schedule will be used for all subsequent schedules and point-in-time recovery (PITR).
-
When creating a 1-node MongoDB cluster, the cluster temporarily enters an Error state instead of Initializing before transitioning to the Ready state.
-
When restoring a MySQL database from a backup, the process may fail if the database name is too long. Use a shorter name for the restored database.
Get expert help¶
If you need assistance, visit the community forum for comprehensive and free database knowledge, or contact our Percona Database Experts for professional support and services.